To say goodbye to FDM 3D printing is a bittersweet moment for 3D People. Our entry into the additive manufacturing industry was marked by the acquisition of two desktop FDM machines in 2015. While we are excited to focus exclusively on industrial additive manufacturing technologies, we do so with a heavy heart as we bid farewell to FDM.
What is FDM technology?
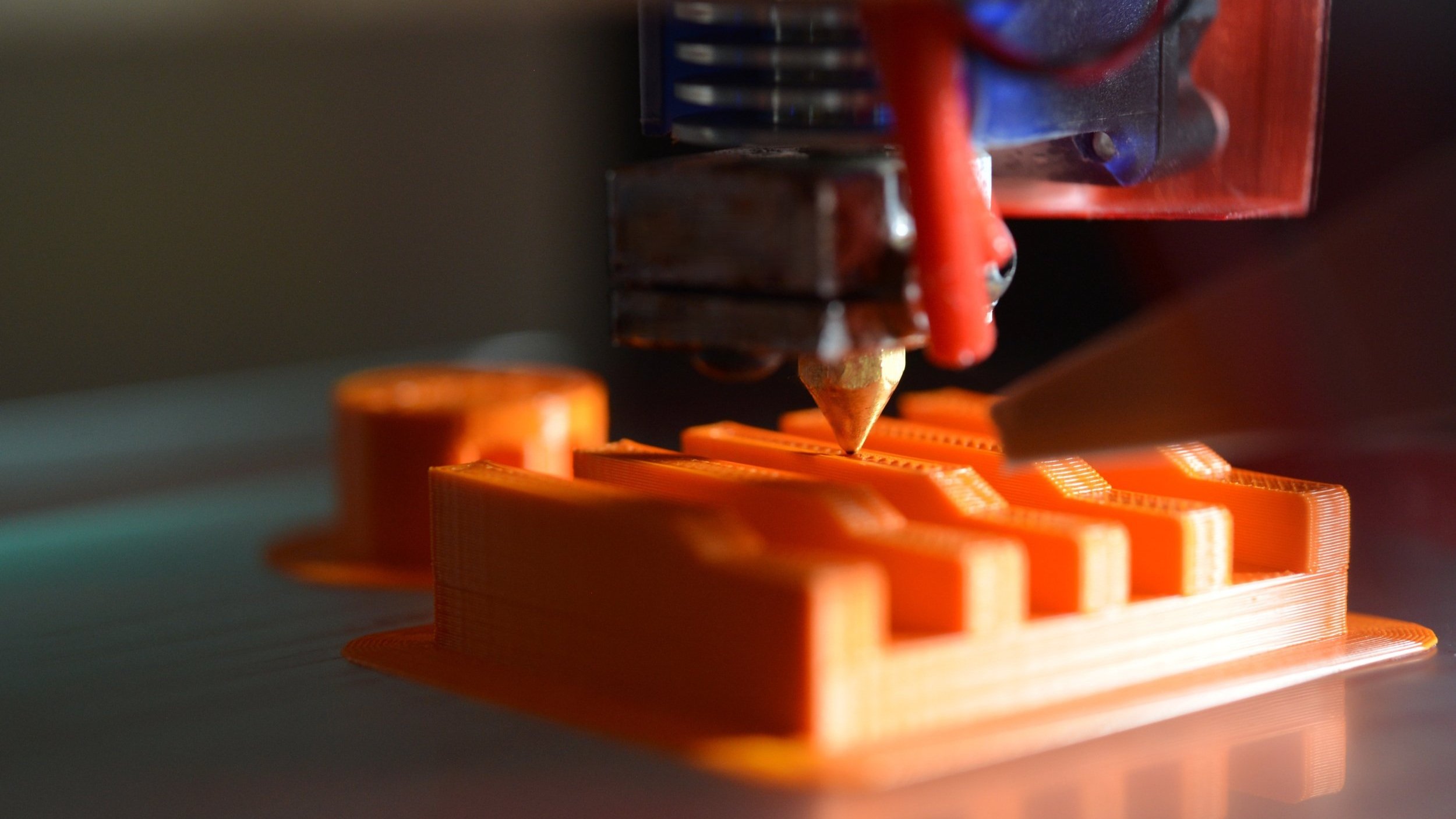
3D printing in PLA (FDM) material
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is the most ubiquitous form of 3D printing available today, encompassing both cost-effective desktop machines and larger industrial-grade ones. Essentially, this additive manufacturing process involves the extrusion of a thermoplastic from a nozzle to build up parts layer by layer.
Why discontinue FDM?
The decision to discontinue FDM printing is based on a range of factors:
Limiting for production parts: At 3D People, our mission is to provide manufacturing services that produce functional, end-use parts. However, the materiality, production speed, and reliability of FDM technology restrict the range of designs that can be feasibly produced.
Quality falls short of our standards: We constantly strive to improve the quality, reliability, and consistency of our manufacturing services. In order to meet our quality standards, FDM parts often have to be declined or reworked several times. To maintain the highest standards of service for our customers, we can not continue to offer FDM printing.
Small parts are expensive: With FDM technology, each small part requires individual setup, printing, and processing time, making the production process more expensive than with other technologies. Small Powder Bed Fusion (PBF) parts are more economical to produce, perform better and have better resolution than their FDM counterparts, there is rarely a justification to offer FDM services for small components.
Limited geometries: Unlike PBF technologies, FDM printing requires support material, which can restrict the types of designs that can be produced and often results in parts with defective surfaces.
Alternative materials are available: PLA material and TPU are examples of bioplastics and flexible elastomers that were not previously available with our PBF offering. However, with the introduction of PA11 Nylon (MJF) - a material derived from castor beans - and TPU (MJF), we can continue to offer services that meet these requirements.
Which materials have been discontinued?
As of February 2023, PLA (FDM) and TPU (FDM) are no longer available to order from 3D People.
PLA (FDM) is a type of thermoplastic material derived from natural, renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional plastics. PLA 3D prints are rigid, low cost, and available with short lead times. The material is available in a variety of colours.
TPU (FDM) is a flexible elastomer with shore hardness 95A. TPU parts behave similarly to rubber with excellent compression and flexibility. These durable 3D prints can withstand cyclic bending without cracking.
What alternative materials are available for PLA?
PA12 Nylon (PBF) is a versatile thermoplastic with properties that enable the material to be used in place of PLA for most applications. PA12 Nylon (SLS) and PA12 Nylon (MJF) are both available to order through the instant quote platform.
PA11 Nylon (PBF) is a thermoplastic that behaves similarly to PA12 Nylon. However, it is more ductile and has a lower heat deflection temperature. PA11 Nylon is derived from natural, renewable resources such as castor beans, making it a suitable alternative to PLA for those looking for Ga more eco-friendly alternative. PA11 Nylon is available on request; get in touch by email or submit an enquiry for a quotation.
What alternative materials are available for TPU (FDM)?
Ultrasint TPU01 (PBF) is a thermoplastic polyurethane material produced by BASF. It is known for its high flexibility, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, making it a popular choice for the production of parts and components that require soft touch and flexibility, such as seals, gaskets, and functional prototypes. It is commonly used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and healthcare. Ultrasint TPU01 (MJF) is available on request; get in touch by email for a quotation.
Where can I get FDM 3D prints now?
We recognise that this change may not be suitable for everyone, as there may be specific applications that are better suited for FDM 3D printing. If you are interested in producing parts that were previously ordered from us, there are a few options available:
Option 1: Purchase a desktop FDM 3D printer
For those who prefer to print parts in-house, a desktop FDM 3D printer may be a good option. While more affordable machines may require some maintenance and technical knowledge to operate, there are user-friendly desktop machines available that are intuitive and easy to maintain.
Option 2: Use an FDM 3D printing service bureau
While we will no longer offer FDM 3D prints, there are other reputable companies that provide PLA and TPU (FDM) 3D printing services. These companies can provide high-quality 3D prints that meet your specific needs.
You can find out more about the materials we offer here.
We'd love to hear your feedback, drop us an email at print@3dpeople.uk and let us know how this change affects you.